Integrate your media app with HomePod
Description: Learn how people can interact with your media app directly from HomePod. We'll show you how to add a media intent to your iPhone or iPad app and help people stream your content to a HomePod speaker over AirPlay simply by using their voice. Explore implementation details and get tips and best practices on how to create a great experience for music, audiobooks, podcasts, meditations, or other media types. To learn more about creating a great AirPlay experience, check out "Tune up your AirPlay audio experience” from WWDC23.
Overview
Overview of the data flow when requesting Siri to play a song via HomePod:
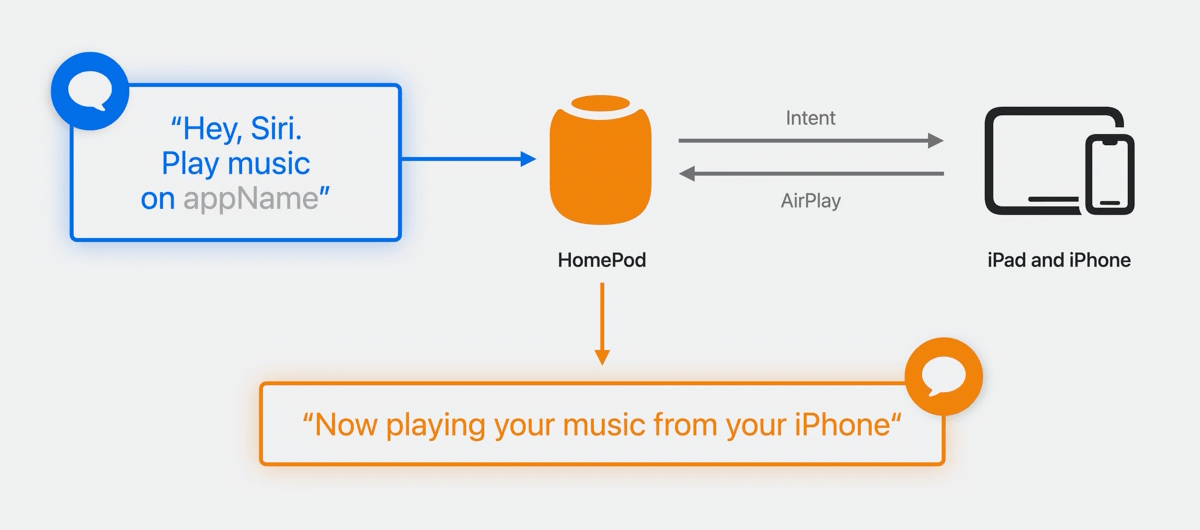
- The device must be connected to the same network as the HomePod.
- The device doesn't need to be physically near the person who is speaking.
- Any app supporting SiriKit Media Intents today will be able to use this capability with no additional changes.
- Supported options:
- Play media
- Music, audiobooks, podcasts, radio, meditation, and more.
- Add to playlist or library
- Show affinity (e.g. like/dislike)
- "Add to playlist" and "like/dislike" actions will use voice recognition to identify the user, and the user's primary device (as configured on Find My) will be used to perform the action.
- Play media
Example requests


Example code to resolve intents
class IntentHandler: INExtension, INPlayMediaIntentHandling {
// INPlayMediaIntent methods
func resolveMediaItems(for intent: INPlayMediaIntent, with completion: @escaping ([INPlayMediaMediaItemResolutionResult]) -> Void) {
guard intent.mediaSearch?.mediaType != .genre else {
return completion([INPlayMediaMediaItemResolutionResult.unsupported(forReason: .unsupportedMediaType) ])
}
if intent.mediaSearch?.mediaName == "push it" {
let item = INMediaItem(identifier: "sample", title: "Push it", type: song, artwork: nil)
return completion(INPlayMediaMediaItemResolutionResult.successes(with: [item]))
}
completion([INPlayMediaMediaItemResolutionResult.unsupported()])
}
}
When handling intent, you can return two types of responses, .handleInApp, which will instruct the system to start the app and play in the background, and .continueInApp, which does the same in foreground. To offer a better experience, handle the request in backgroud using .handleInApp since it doesn't require the user to unlock their phone.
Make sure your app responds all intents as fast as possible. Requests will timeout after 10 seconds.
 Twitter
Twitter
 GitHub
GitHub
 www.roger.ml
www.roger.ml